All Specialties For Doppler Ultrasonography Recover Your Auditory And Balanced Health!
All Specialties For Doppler Ultrasonography Recover Your Auditory And Balanced Health!
Doppler Ultrasonography
Transcranial and Extracranial
Ninety percent of our patients consume dizziness with a previous diagnosis attributable to cervical spine problems. The ability to measure the cerebral circulatory dynamics allows us to observe that 15% of this group presents dizziness of cervical cause by variations in the flow of the vertebral artery and 60% of supratrochlear artery terminal branch of the internal carotid artery, 15% of the anterior cerebral artery, also terminal and ascent of vestibular nuclei, hence the importance of knowing the intracerebral arterial flow.
Among the causes of neuropathological diseases, vascular diseases predominate, therefore we introduce non-invasive methods into the daily routine, in order to study the cerebral circulatory dynamics.
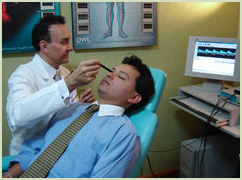
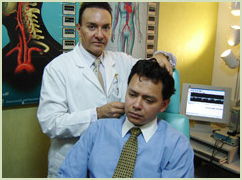
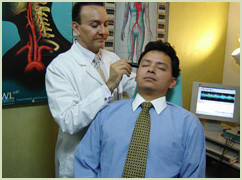
With Sonotechnik equipment for transcranial and extracranial doppler we studied the cerebral circulatory dynamics with Doppler Ultrasonography USD, which consists in supporting a probe on the cranial surface capable of emitting sounds at a frequency (variable according to the depth of the artery in study).
The sound is reflected by the column of erythrocytes (red blood cells) that circulate through the artery, which allows computer methods to evaluate different arterial parameters:
- speed
- flow
- Direction of the bloodstream
- Peripheral resistance
- Degrees of stenosis (occlusion)
According to the depth of the cerebral arteries to be studied, the Doppler ultrasonography may be oriented to the extracranial arteries -USD Extracranial-, or to the arteries that are inside the skull -USD Transcranial.
Ultrasonography DFMareos treatment.
Doppler Ultrasonography Techniques:
* Eco-doppler of supraortic trunks (TSA)
* Doppler of TSA and transcranial (CT).
Both techniques are complementary and if possible, should be performed routinely in all patients with imbalance. They allow us to identify the cases with:
A) Ischemias or occlusions of cerebral arteries:
Occlusion of extracranial internal carotid artery (ICA), also assessing its hemodynamic repercussion and intracranial substitutions.
Significant stricture of extracranial carotid artery.
Proximal intracranial arterial stenosis.
Occlusion of ACM (in its M1 portion) and its possible spontaneous recanalization or thrombolysis. In patients with cerebral artery occlusion, the CT Doppler also allows the assessment of the leptomeningeal replacement that has been established, which has an important prognostic value.
Cerebral microangiopathy (a generalized increase of the peripheral resistances is observed).
Presence of microemulses in ACM in cases of emboligenic cardiopathy and / or atheromatous stenosis of extracranial ACI.
Permeable ovoid foramen, through the detection of air microbubbles in the ACM, after intravenous injection of saline serum previously agitated with air and the patient performed a Valsalva
B) Hyperflows or hyperflows of arteries:
Dizziness and vertigo, otoneurologo DFE The supraorbital flow is the result of the hydrodynamic compensation between the internal and external carotid system. The vertebral arteries along with the internal carotids are responsible for irrigating the brain stem, seat of the centers of coordination of balance.
The prevalence of significant stenosis of the internal carotid artery is related to age, sex and risk factors such as smoking, diabetes, hypertension and hypercholesterolemia.
Atherosclerosis of the ABDOMINAL aorta develops early and the carotid and coronary arteries are affected five to ten years later.
Carotid atherosclerosis has a marked tendency to develop in the bifurcation at the level of the carotid artery, extending to 2 cm in the cephalic direction towards the origin of the internal carotid artery, this phenomenon can happen without provoking symptoms, and be the Source of microembolisms at the higher level.
Using Doppler ultrasound, a prevalence greater than 50% has been found in the population between 45 and 65 years old with 3 to 7%.
When studying 2,500 patients with vertigo, Bertora and Bergmann found that 48.16% of the cases have antecedents of vascular origin predominating within this group the pathologies secondary to processes of vascular origin predominated within this group the pathological ones secondary to processes of hydrodynamic alterations within Of the capillary with 20.92% for hypotension and 20.34% for hypertension. In our study (1500 patients) we have similar results. The vertigo symptom may occur in 90% of cases in any of its manifestations.